- Home
- About
- Promotions
-
Products
-
Elisa Kits
- |
-
Primary antibodies
- |
-
Secondary antibodies
- |
-
Proteins
- |
-
IHC reagents
- |
-
WB reagents
- PonceauS Staining Solution
- PBST Washing Buffer, 10X
- 1.5M Tris-HCl Buffer, pH8.8
- 1M Tris-HCl Buffer, pH6.8
- 10% SDS Solution
- Prestained Protein Marker
- TBST Washing Buffer, 10X
- SDS PAGE Loading Buffer, 5X
- Stripping Buffered Solution
- Tris Buffer, pH7.4, 10X
- Total Protein Extraction Kit
- Running Buffer, 10X
- Transfer Buffer, 10X
- 30% Acr-Bis(29:1) Solution
- Tris电泳液速溶颗粒
- PBS(1X, premixed powder)
- TBS(1X, premixed powder)
- 快速封闭液
- 转膜液速溶颗粒
- Chemical reagents
- News
- Distributor
- Resources
- Contact
- Home
- >
- Info
- >
- Leptin mouse mAb
- >
- Go Back
Leptin mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM1446
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Fields:
- >>Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction;>>Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction;>>AMPK signaling pathway;>>JAK-STAT signaling pathway;>>Adipocytokine signaling pathway;>>Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant full length of human Leptin protein expressed in E.coli.
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects human Leptin proteins.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- ELISA 1:10000-20000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from mouse ascites by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- FLJ94114;LEP;LEP_HUMAN;LEPD;Leptin (murine obesity homolog);Leptin (obesity homolog, mouse);Leptin;Leptin Murine Obesity Homolog;Leptin Precursor Obesity Factor;OB;Obese Protein;Obese, mouse, homolog of;Obesity;Obesity factor;Obesity factor;Obesity homolog mouse;Obesity Murine Homolog Leptin;OBS;OTTHUMP00000212285.
- Background:
- This gene encodes a protein that is secreted by white adipocytes, and which plays a major role in the regulation of body weight. This protein, which acts through the leptin receptor, functions as part of a signaling pathway that can inhibit food intake and/or regulate energy expenditure to maintain constancy of the adipose mass. This protein also has several endocrine functions, and is involved in the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses, hematopoiesis, angiogenesis and wound healing. Mutations in this gene and/or its regulatory regions cause severe obesity, and morbid obesity with hypogonadism. This gene has also been linked to type 2 diabetes mellitus development. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in LEP may be a cause of autosomal recessive obesity [MIM:601665].,function:May function as part of a signaling pathway that acts to regulate the size of the body fat depot. An increase in the level of LEP may act directly or indirectly on the CNS to inhibit food intake and/or regulate energy expenditure as part of a homeostatic mechanism to maintain constancy of the adipose mass.,online information:Leptin entry,similarity:Belongs to the leptin family.,subunit:Interacts with SIGLEC6.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Secreted .
- Expression:
- Adipose tissue is the main source of leptin. It is also produced by other peripheral tissues such as the skeletal muscle (PubMed:7789654, PubMed:16052473, PubMed:12448771). Expressed by intercalated and striated tracts of submandibular and parotid salivary gland intralobular ducts (PubMed:12448771). Detected by fundic epithelium of the gastric mucosa (PubMed:10896907). Secreted into blood and gastric juice (PubMed:10896907).
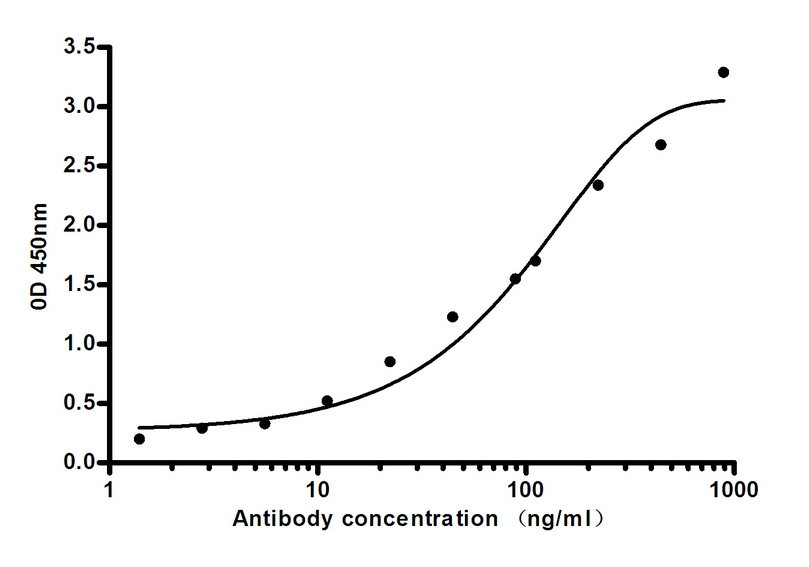
- Indirect ELISA assay for anti-Leptin mouse mAb.Antigen coating concentration: 4ug/ml.




