IL-1α Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0368
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- IL-1α
- Fields:
- >>MAPK signaling pathway;>>Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction;>>Necroptosis;>>Cellular senescence;>>Osteoclast differentiation;>>Hematopoietic cell lineage;>>Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease;>>AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications;>>Type I diabetes mellitus;>>Alzheimer disease;>>Prion disease;>>Pathways of neurodegeneration - multiple diseases;>>Pertussis;>>Leishmaniasis;>>Tuberculosis;>>Measles;>>Influenza A;>>Inflammatory bowel disease;>>Rheumatoid arthritis;>>Graft-versus-host disease;>>Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis
- Gene Name:
- IL1A
- Protein Name:
- Interleukin-1 alpha
- Human Gene Id:
- 3552
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P01583
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P01582
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of human IL-1a expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- IL-1α Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of IL-1α protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- IL1A;IL1F1;Interleukin-1 alpha;IL-1 alpha;Hematopoietin-1
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 31kD
- References:
- 1. Du,Y.; et al. 2000. Neurology 55: 480-484.
2. Grimaldi, L. et al. Ann. Neurol. 47: 361-365, 2000.
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the interleukin 1 cytokine family. This cytokine is a pleiotropic cytokine involved in various immune responses, inflammatory processes, and hematopoiesis. This cytokine is produced by monocytes and macrophages as a proprotein, which is proteolytically processed and released in response to cell injury, and thus induces apoptosis. This gene and eight other interleukin 1 family genes form a cytokine gene cluster on chromosome 2. It has been suggested that the polymorphism of these genes is associated with rheumatoid arthritis and Alzheimer's disease. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- domain:The similarity among the IL-1 precursors suggests that the amino ends of these proteins serve some as yet undefined function.,function:Produced by activated macrophages, IL-1 stimulates thymocyte proliferation by inducing IL-2 release, B-cell maturation and proliferation, and fibroblast growth factor activity. IL-1 proteins are involved in the inflammatory response, being identified as endogenous pyrogens, and are reported to stimulate the release of prostaglandin and collagenase from synovial cells.,online information:Interleukin-1 entry,online information:The Singapore human mutation and polymorphism database,similarity:Belongs to the IL-1 family.,subcellular location:The lack of a specific hydrophobic segment in the precursor sequence suggests that IL-1 is released by damaged cells or is secreted by a mechanism differing from that used for other secretory proteins.,subunit:Mono
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Secreted . The lack of a specific hydrophobic segment in the precursor sequence suggests that IL-1 is released by damaged cells or is secreted by a mechanism differing from that used for other secretory proteins. The secretion is dependent on protein unfolding and facilitated by the cargo receptor TMED10; it results in protein translocation from the cytoplasm into the ERGIC (endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment) followed by vesicle entry and secretion (PubMed:32272059). .
- Expression:
- Lung,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
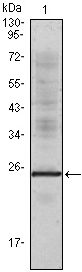
- Western Blot analysis using IL-1α Monoclonal Antibody against truncated IL-1α recombinant protein.



