Btk Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0083
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Monkey
- Target:
- Btk
- Fields:
- >>NF-kappa B signaling pathway;>>Osteoclast differentiation;>>Platelet activation;>>B cell receptor signaling pathway;>>Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway;>>Epstein-Barr virus infection;>>Primary immunodeficiency
- Gene Name:
- BTK
- Protein Name:
- Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK
- Human Gene Id:
- 695
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q06187
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P35991
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of Btk expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- Btk Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Btk protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:200 - 1:1000. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- BTK;AGMX1;ATK;BPK;Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK;Agammaglobulinaemia tyrosine kinase;ATK;B-cell progenitor kinase;BPK;Bruton tyrosine kinase
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 76kD
- References:
- 1. Yamada, N., et al. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 192: 231-240.
2. Thomas, J.D., et al. 1993. Science. 261: 355-358.
3. Tamagnone, L., et al. Oncogene 9: 3683-3688.
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene plays a crucial role in B-cell development. Mutations in this gene cause X-linked agammaglobulinemia type 1, which is an immunodeficiency characterized by the failure to produce mature B lymphocytes, and associated with a failure of Ig heavy chain rearrangement. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2013],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:ATP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine = ADP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine phosphate.,cofactor:Binds 1 zinc ion per subunit.,disease:Defects in BTK are the cause of X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) [MIM:300755]; also called X-linked agammaglobulinemia type 1 (AGMX1) or immunodeficiency type 1 (IMD1). XLA is a humoral immunodeficiency disease which results in developmental defects in the maturation pathway of B-cells. Affected boys have normal levels of pre-B-cells in their bone marrow but virtually no circulating mature B-lymphocytes. This results in a lack of immunoglobulins of all classes and leads to recurrent bacterial infections like otitis, conjunctivitis, dermatitis, sinusitis in the first few years of life, or even some patients present overwhelming sepsis or meningitis, resulting in death in a few hours. Treatment in most cases is by infusion of intravenous immunoglobulin.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Nucleus. In steady state, BTK is predominantly cytosolic. Following B-cell receptor (BCR) engagement by antigen, translocates to the plasma membrane through its PH domain. Plasma membrane localization is a critical step in the activation of BTK. A fraction of BTK also shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, and nuclear export is mediated by the nuclear export receptor CRM1.
- Expression:
- Predominantly expressed in B-lymphocytes.
Characterization of Tumor Microenvironment in Lung Adenocarcinoma Identifies Immune Signatures to Predict Clinical Outcomes and Therapeutic Responses. Frontiers in Oncology Front Oncol. 2021 Mar;0:356 IHC Human 1 : 400 Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD)
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
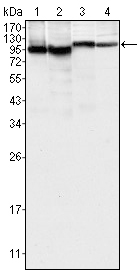
- Western Blot analysis using Btk Monoclonal Antibody against K562 (1), MCF-7 (2), Jurkat (3) and HEK293 (4) cell lysate.
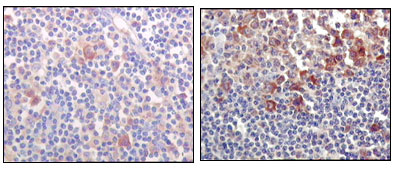
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human lymph-node tissues (left) and human lymph follicle tissues (right), showing cytoplasmic and membrane localization with DAB staining using Btk Monoclonal Antibody.
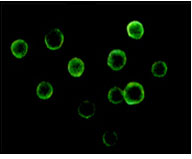
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Jurkat cells using Btk Monoclonal Antibody.



