BPTF Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0080
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- BPTF
- Gene Name:
- BPTF
- Protein Name:
- Nucleosome-remodeling factor subunit BPTF
- Human Gene Id:
- 2186
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q12830
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of human BPTF expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- BPTF Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of BPTF protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
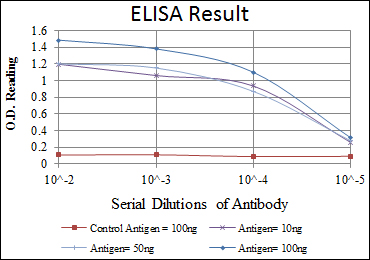
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- BPTF;FAC1;FALZ;Nucleosome-remodeling factor subunit BPTF;Bromodomain and PHD finger-containing transcription factor;Fetal Alz-50 clone 1 protein;Fetal Alzheimer antigen
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 338kD
- References:
- 1. PLoS Genet. 2008 Oct;4(10):e1000241.
2. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008 Mar;7(3):499-508.
- Background:
- This gene was identified by the reactivity of its encoded protein to a monoclonal antibody prepared against brain homogenates from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Analysis of the original protein (fetal Alz-50 reactive clone 1, or FAC1), identified as an 810 aa protein containing a DNA-binding domain and a zinc finger motif, suggested it might play a role in the regulation of transcription. High levels of FAC1 were detected in fetal brain and in patients with neurodegenerative diseases. The protein encoded by this gene is actually much larger than originally thought, and it also contains a C-terminal bromodomain characteristic of proteins that regulate transcription during proliferation. The encoded protein is highly similar to the largest subunit of the Drosophila NURF (nucleosome remodeling factor) complex. In Drosophila, the NURF complex, which catalyzes nucleosome
- Function:
- developmental stage:Abundantly expressed in the fetal brain. Present throughout the gray and white matter of the developing spinal cord at 18-22 gestational weeks. Expressed at low levels in adult brain and spinal cord and reexpressed in neurodegenerative diseases (at protein level).,domain:The second PHD-type zinc finger mediates binding to histone H3-K4Me3.,function:Histone-binding component of NURF (nucleosome-remodeling factor), a complex which catalyzes ATP-dependent nucleosome sliding and facilitates transcription of chromatin. Specifically recognizes H3 tails trimethylated on 'Lys-4' (H3-K4Me3), which mark transcription start sites of virtually all active genes. May also regulate transcription through direct binding to DNA or transcription factors.,miscellaneous:Highly susceptible to proteolysis.,PTM:Phosphorylation enhances DNA-binding. Phosphorylated upon DNA damage, probably by
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm. Nucleus. In brains of Alzheimer disease patients, present in a subset of amyloid-containing plaques.
- Expression:
- Ubiquitously expressed, with highest levels in testis. Present in kidney, liver and brain. In the brain, highest levels are found in motor cortex (at protein level).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis using BPTF Monoclonal Antibody against HEK293 (1) and BPTF (AA: 503-670)-hIgGFc transfected HEK293 (2) cell lysate.