AR Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0043
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- Androgen Receptor
- Fields:
- >>Oocyte meiosis;>>Pathways in cancer;>>Chemical carcinogenesis - receptor activation;>>Prostate cancer
- Gene Name:
- AR
- Protein Name:
- Androgen receptor
- Human Gene Id:
- 367
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P10275
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P19091
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of AR (aa689-919) expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- AR Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of AR protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- AR;DHTR;NR3C4;Androgen receptor;Dihydrotestosterone receptor;Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 4
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 99kD
- References:
- 1. Cancer Res. 2006 Nov 15;66(22):11077-83.
2. Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Oct;27(20):7125-42.
- Background:
- The androgen receptor gene is more than 90 kb long and codes for a protein that has 3 major functional domains: the N-terminal domain, DNA-binding domain, and androgen-binding domain. The protein functions as a steroid-hormone activated transcription factor. Upon binding the hormone ligand, the receptor dissociates from accessory proteins, translocates into the nucleus, dimerizes, and then stimulates transcription of androgen responsive genes. This gene contains 2 polymorphic trinucleotide repeat segments that encode polyglutamine and polyglycine tracts in the N-terminal transactivation domain of its protein. Expansion of the polyglutamine tract from the normal 9-34 repeats to the pathogenic 38-62 repeats causes spinal bulbar muscular atrophy (Kennedy disease). Mutations in this gene are also associated with complete androgen insensitivity (CAIS). Two alternatively spliced variants encoding distinct isoform
- Function:
- disease:Defects in AR are the cause of androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS) [MIM:300068]; previously known as testicular feminization syndrome (TFM). AIS is an X-linked recessive form of pseudohermaphroditism due end-organ resistance to androgen. Affected males have female external genitalia, female breast development, blind vagina, absent uterus and female adnexa, and abdominal or inguinal testes, despite a normal 46,XY karyotype.,disease:Defects in AR are the cause of androgen insensitivity syndrome partial (PAIS) [MIM:312300]; also known as Reifenstein syndrome. PAIS is characterized by hypospadias, hypogonadism, gynecomastia, genital ambiguity, normal XY karyotype, and a pedigree pattern consistent with X-linked recessive inheritance. Some patients present azoospermia or severe oligospermia without other clinical manifestations.,disease:Defects in AR are the cause of spinal and bulb
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus . Cytoplasm . Detected at the promoter of target genes (PubMed:25091737). Predominantly cytoplasmic in unligated form but translocates to the nucleus upon ligand-binding. Can also translocate to the nucleus in unligated form in the presence of RACK1. .
- Expression:
- [Isoform 2]: Mainly expressed in heart and skeletal muscle. ; [Isoform 3]: Expressed in basal and stromal cells of the prostate (at protein level).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
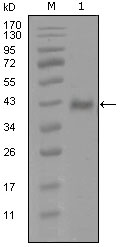
- Western Blot analysis using AR Monoclonal Antibody against truncated Trx-AR recombinant protein (1).



