Cleaved-Thrombin APII (R327) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YC0077
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Rat;Mouse;
- Target:
- Thrombin APII
- Fields:
- >>Phospholipase D signaling pathway;>>Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction;>>Complement and coagulation cascades;>>Platelet activation;>>Regulation of actin cytoskeleton;>>Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection;>>Coronavirus disease - COVID-19;>>Pathways in cancer
- Gene Name:
- F2
- Protein Name:
- Prothrombin
- Human Gene Id:
- 2147
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P00734
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P19221
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human THRB. AA range:278-327
- Specificity:
- Cleaved-Thrombin APII (R327) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of fragment of activated Thrombin APII protein resulting from cleavage adjacent to R327.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:20000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- F2;Prothrombin;Coagulation factor II
- Observed Band(KD):
- 19kD
- Background:
- Coagulation factor II is proteolytically cleaved to form thrombin in the first step of the coagulation cascade which ultimately results in the stemming of blood loss. F2 also plays a role in maintaining vascular integrity during development and postnatal life. Peptides derived from the C-terminus of this protein have antimicrobial activity against E. coli and P. aeruginosa. Mutations in F2 lead to various forms of thrombosis and dysprothrombinemia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:Selective cleavage of Arg-|-Gly bonds in fibrinogen to form fibrin and release fibrinopeptides A and B.,disease:Defects in F2 are the cause of various forms of dysprothrombinemia [MIM:176930].,disease:Genetic variations in F2 may be a cause of susceptibility to ischemic stroke [MIM:601367]; also known as cerebrovascular accident or cerebral infarction. A stroke is an acute neurologic event leading to death of neural tissue of the brain and resulting in loss of motor, sensory and/or cognitive function. Ischemic strokes, resulting from vascular occlusion, is considered to be a highly complex disease consisting of a group of heterogeneous disorders with multiple genetic and environmental risk factors.,function:Thrombin, which cleaves bonds after Arg and Lys, converts fibrinogen to fibrin and activates factors V, VII, VIII, XIII, and, in complex with thrombomodulin, protei
- Subcellular Location:
- Secreted, extracellular space.
- Expression:
- Expressed by the liver and secreted in plasma.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Cleaved-Thrombin APII (R327) Polyclonal Antibody
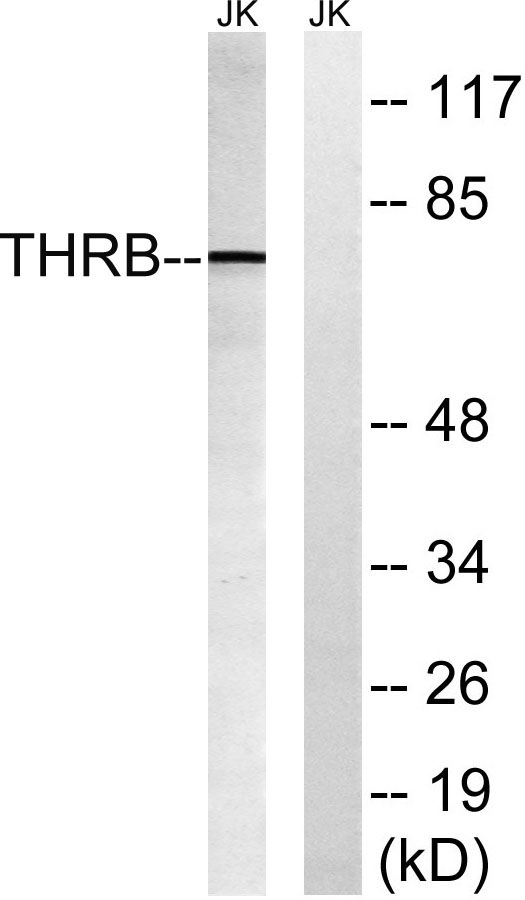
- Western blot analysis of lysates from Jurkat cells, treated with etoposide 25uM 24H, using THRB (AP2,Cleaved-Arg327) Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



