Total Synuclein-pan Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA4383C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
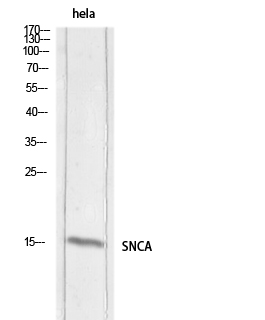
- SNCA
- Human Gene Id:
- 6622
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P37840
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- O55042
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P37377
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Alpha-synuclein (Non-A beta component of AD amyloid) (Non-A4 component of amyloid precursor) (NACP)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- alternative products:Additional isoforms seem to exist,disease:Brain iron accumulation type 1 (NBIA1, also called Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome), a rare neuroaxonal dystrophy, is histologically characterized by axonal spheroids, iron deposition, Lewy body (LB)-like intraneuronal inclusions, glial inclusions and neurofibrillary tangles. SNCA is found in LB-like inclusions, glial inclusions and spheroids.,disease:Defects in SNCA are a cause of autosomal dominant Parkinson disease 1 (PARK1) [MIM:168601, 168600]. Parkinson disease (PD) is a complex, multifactorial disorder that typically manifests after the age of 50 years, although early-onset cases (before 50 years) are known. PD generally arises as a sporadic condition but is occasionally inherited as a simple mendelian trait. Although sporadic and familial PD are very similar, inherited forms of the disease usually begin at earlier ages and are associated with atypical clinical features. PD is characterized by bradykinesia, resting tremor, muscular rigidity and postural instability, as well as by a clinically significant response to treatment with levodopa. The pathology involves the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and the presence of Lewy bodies (intraneuronal accumulations of aggregated proteins), in surviving neurons in various areas of the brain.,disease:Defects in SNCA are the cause of Lewy body dementia (DLB) [MIM:127750]. DLB is a neurodegenerative disorder clinically characterized by dementia and parkinsonism, often with fluctuating cognitive function, visual hallucinations, falls, syncopal episodes, and sensitivity to neuroleptic medication. Presence of Lewy bodies are the only essential pathologic features.,disease:Defects in SNCA are the cause of Parkinson disease 4 (PARK4) [MIM:605543, 168600].,disease:Deposition of fibrillar amyloid proteins intraneuronally as neurofibrillary tangles is characteristic of Alzheimer disease (AD). SNCA is a minor protein found within these deposits, but a major non amyloid component.,domain:The NAC domain is involved in the fibril formation. The middle region forms the core of the filaments. The C-terminus may regulate aggregation and determine the diameter of the filaments.,function:May be involved in the regulation of dopamine release and transport. Soluble protein, normally localized primarily at the presynaptic region of axons, which can form filamentous aggregates that are the major non amyloid component of intracellular inclusions in several neurodegenerative diseases (synucleinopathies). Induces fibrillization of microtubule-associated protein tau. Reduces neuronal responsiveness to various apoptotic stimuli, leading to a decreased caspase-3 activation.,PTM:Hallmark lesions of neurodegenerative synucleinopathies contain alpha-synuclein that is modified by nitration of tyrosine residues and possibly by dityrosine cross-linking to generated stable oligomers.,PTM:Phosphorylated, predominantly on serine residues. Phosphorylation by CK1 appears to occur on residues distinct from the residue phosphorylated by other kinases. Phosphorylation of Ser-129 is selective and extensive in synucleinopathy lesions. In vitro, phosphorylation at Ser-129 promoted insoluble fibril formation. Phosphorylated on Tyr-125 by a PTK2B-dependent pathway upon osmotic stress.,PTM:Ubiquitinated. The predominant conjugate is the diubiquitinated form.,similarity:Belongs to the synuclein family.,subcellular location:Membrane-bound in dopaminergic neurons. Also found in the nucleus.,subunit:Soluble monomer which can form filamentous aggregates. Interacts with UCHL1 (By similarity). Interacts with phospholipase D and histones.,tissue specificity:Expressed principally in brain but is also expressed in low concentrations in all tissues examined except in liver. Concentrated in presynaptic nerve terminals.,
- Function:
- microglial cell activation, cell activation, regulation of receptor recycling, positive regulation of receptor recycling,positive regulation of neurotransmitter secretion, synaptic transmission, dopaminergic, response to molecule of bacterial origin, myeloid leukocyte activation, regulation of leukocyte activation, generation of precursor metabolites and energy, oxidative phosphorylation, cellular amino acid derivative metabolic process, biogenic amine metabolic process, catecholamine metabolic process, fatty acid metabolic process, neutral lipid metabolic process, phospholipid metabolic process, phosphorus metabolic process, phosphate metabolic process, cellular ion homeostasis,endocytosis, receptor-mediated endocytosis, anti-apoptosis, defense response, immune response, response to oxidative stress, mitochondrion organization, mitochondrial membrane organization, cell-cell signaling, s
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Membrane . Nucleus . Cell junction, synapse . Secreted . Cell projection, axon . Membrane-bound in dopaminergic neurons (PubMed:15282274). Expressed and colocalized with SEPTIN4 in dopaminergic axon terminals, especially at the varicosities (By similarity). .
- Expression:
- Highly expressed in presynaptic terminals in the central nervous system. Expressed principally in brain.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs