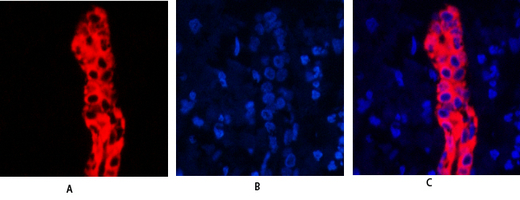
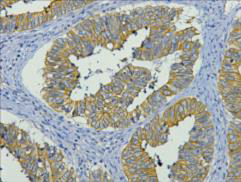
Total Cytokeratin 19 Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA3306C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
- KRT19
- Human Gene Id:
- 3880
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P08727
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P19001
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q63279
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 19 (Cytokeratin-19) (CK-19) (Keratin-19) (K19)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- developmental stage:Present in hair follicles at all stages of development.,domain:This keratin differs from all other IF proteins in lacking the C-terminal tail domain.,function:Involved in the organization of myofibers. Together with KRT8, helps to link the contractile apparatus to dystrophin at the costameres of striated muscle.,miscellaneous:There are two types of cytoskeletal and microfibrillar keratin: I (acidic; 40-55 kDa) and II (neutral to basic; 56-70 kDa).,similarity:Belongs to the intermediate filament family.,subunit:Heterotetramer of two type I and two type II keratins. Interacts with PNN and the actin-binding domain of DMD. Interacts with HCV core protein.,tissue specificity:Expressed in a defined zone of basal keratinocytes in the deep outer root sheath of hair follicles. Also observed in sweat gland and mammary gland ductal and secretory cells, bile ducts, gastrointestinal tract, bladder urothelium, oral epithelia, esophagus, ectocervical epithelium (at protein level). Expressed in epidermal basal cells, in nipple epidermis and a defined region of the hair follicle. Also seen in a subset of vascular wall cells in both the veins and artery of human umbilical cord, and in umbilical cord vascular smooth muscle. Observed in muscle fibers accumulating in the costameres of myoplasm at the sarcolemma in structures that contain dystrophin and spectrin.,
- Function:
- cytoskeleton organization, response to endogenous stimulus, response to hormone stimulus, response to organic substance, cellular component assembly involved in morphogenesis, actin filament-based process, actin cytoskeleton organization, myofibril assembly, actomyosin structure organization, cellular component morphogenesis, muscle cell differentiation, response to estrogen stimulus, sarcomere organization, response to steroid hormone stimulus,striated muscle cell differentiation, muscle cell development, striated muscle cell development,
- Expression:
- Expressed in a defined zone of basal keratinocytes in the deep outer root sheath of hair follicles. Also observed in sweat gland and mammary gland ductal and secretory cells, bile ducts, gastrointestinal tract, bladder urothelium, oral epithelia, esophagus, ectocervical epithelium (at protein level). Expressed in epidermal basal cells, in nipple epidermis and a defined region of the hair follicle. Also seen in a subset of vascular wall cells in both the veins and artery of human umbilical cord, and in umbilical cord vascular smooth muscle. Observed in muscle fibers accumulating in the costameres of myoplasm at the sarcolemma in structures that contain dystrophin and spectrin.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs