
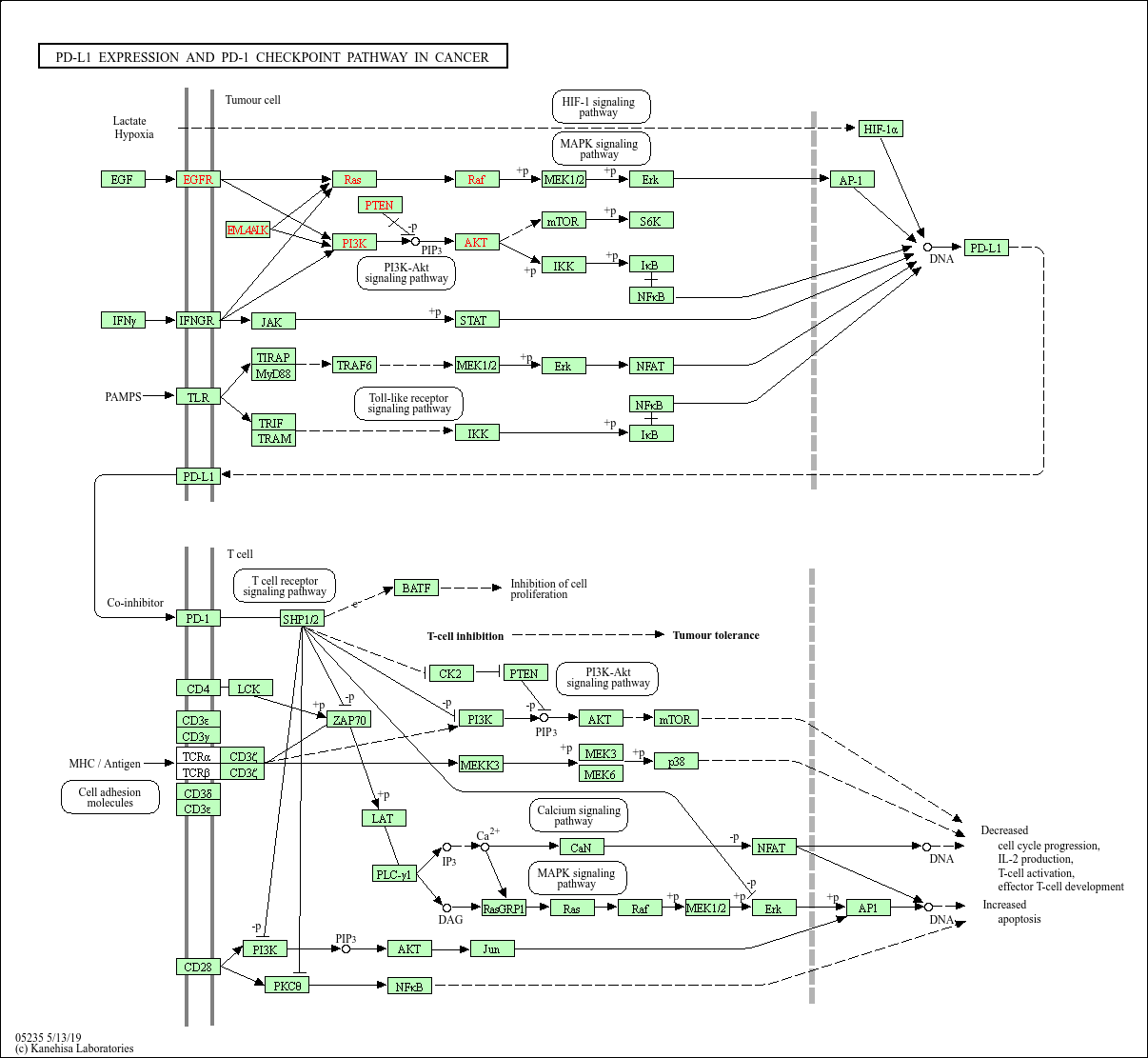
PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer
Programmed cell death 1 (PD1) and its ligand (PDL1) are key regulatory physiological immune checkpoints that maintain self-tolerance in the organism by regulating the degree of activation of T and B cells amongst other immune cell types. In solid tumors, the PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory pathway can be (mis-)used to silence the immune system by increasing the expression of PD-L1 on the tumor cell surface. Up-regulation of PD-L1 is caused by activation of pro-survival pathways MAPK and PI3K/Akt as well as transcriptional factors HIF-1, STAT3 and NF-kappa B. The MAPK and PI3K signalling pathways are activated by gene mutations and growth factors. PD-L1 on tumor cells may then engage the PD-1 receptors resulting in suppression of T-cell mediated immune response. Therapeutic antibodies blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway by targeting PD-L1 or PD-1 are highly effective in rescuing T cell anti-tumor effector functions.
Product List
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Catalog
Product
Reactivity
Applications










